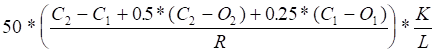
The Swing Index was developed by J. Welles Wilder (New Concepts In Technical Trading Systems, 1978). The Accumulative Swing Index is a cumulative total of the Swing Index.
According to Wilder, the Swing Index seeks to isolate the "real" price by comparing the relationships between the current prices (open, high, low, close) and the previous period's prices. Wilder used this index as the basis for a trend-following system.
The formula for the Swing Index is as follows:
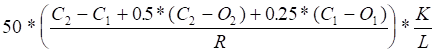
where:
K = the largest absolute value of:
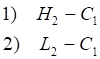
L = Value of a limit move in one direction (use CSpec or the exchange’s web site to look up this value)
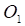 = Previous Bar's Open
= Previous Bar's Open
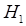 = Previous Bar's High
= Previous Bar's High
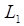 = Previous Bar's Low
= Previous Bar's Low
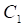 = Previous Bar's Close
= Previous Bar's Close
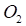 = Current Bar's Open
= Current Bar's Open
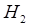 = Current Bar's High
= Current Bar's High
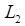 = Current Bar's Low
= Current Bar's Low
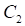 = Current Bar's Close.
= Current Bar's Close.
To obtain "R", first determine the largest absolute value of:
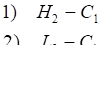
if 1) is the largest,
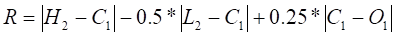
if 2) is the largest,
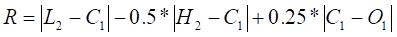
if 3) is the largest,
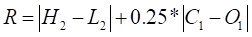
Accumulative Swing Index Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Start Time |
Opens sub-window to identify the earliest bar of the calculation: •Number of bars back from current bar •Date and time •Number of days back from current bar |
|
Display |
Opens sub-window with display parameters: •Color = Line color. •Weight = Line thickness. •Display = Line style: line or histogram. •ShareScale = Determines whether sharing of the vertical scales between studies is accepted. Auto = System determine whether sharing is feasible. On = Scale is shared regardless of the functions and studies displayed. Off = Scale is not shared. ShareScale must be On if study is overlaid on a study with multiple outputs. |
|
MarkIt |
Opens Specify Conditions window. |
|
Price Limit |
Value for scaling the study output. Some commodities have a limit move, which is used to manage volatility, as it limits how much a price can move during the trading day. Limit moves can be defined in terms of price ( e.g. CLE), percent (EP), and basis points (FGZ). Consult CSpec properties to find limit moves for particular commodities. This parameter is used to scale that value. |