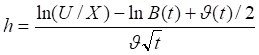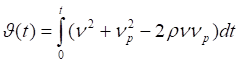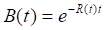 Theoretical value of a call
Theoretical value of a callIn 1973, Merton produced a model with a non-constant interest rate. He assumed that interest rates follow a special type of random process.
By taking into consideration the dynamic process of interest rate determination, and the correlation between the underlying price and the options price, this model provides an improvement over the Black-Scholes model. This model is generally used to value European options written on stocks.
Notation
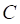 Theoretical value of a call
Theoretical value of a call
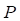 Theoretical value of a put
Theoretical value of a put
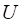 Underlying price
Underlying price
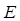 Strike price
Strike price
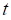 Time to expiration in years
Time to expiration in years
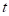 Cumulative normal density
function
Cumulative normal density
function
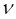 Volatility
Volatility
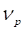 Volatility of an interest rate contract
Volatility of an interest rate contract
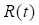 Interest rate
Interest rate
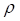 Correlation between the underlying and interest rate contracts
Correlation between the underlying and interest rate contracts
The theoretical values for European calls and puts are:
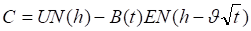
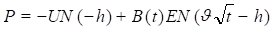
Where: