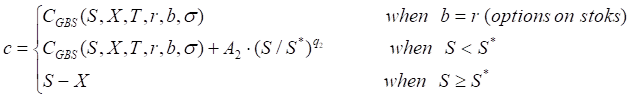
The quadratic approximation method by Baron-Adesi and Whaley (1987) can be used to price American options.
TheoV
Call
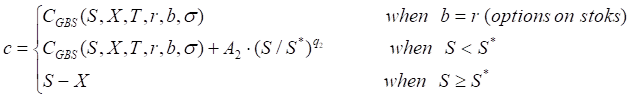
where
b – the cost-of-carry rate;
b = r to price options on stocks.
b = r – q to price options on stocks and stock indexes paying a continuous dividend yield q
b = 0 to price options on futures.
b = r – rf to price currency options (rf – risk-free rate of the foreign currency).
CGBS – the generalized Black-Scholes call TheoV expression;
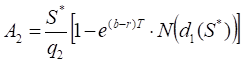
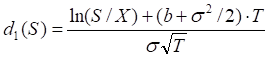
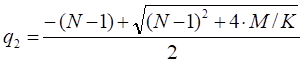
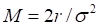
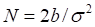
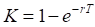
S* – the critical commodity price for the call option that satisfies
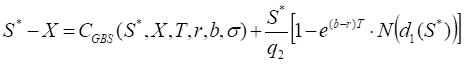
The last equation should be numerically solved to find S*.
Put
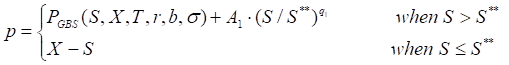
where
PGBS – the generalized Black-Scholes put TheoV expression;
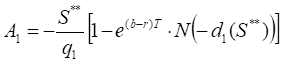
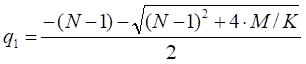
S**– the critical commodity price for the put option that satisfies
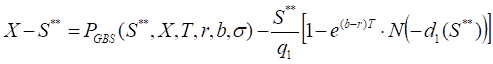
The last equation should be numerically solved to find S**.
Delta
Call
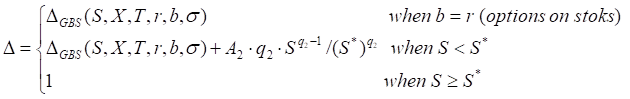
where
∆GBS - the generalized Black-Scholes call ∆ expression.
Put
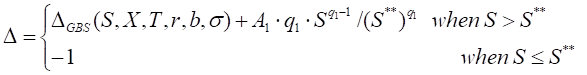
where
∆GBS - the generalized Black-Scholes put ∆ expression.
Gamma
Call
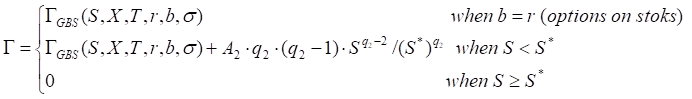
Put
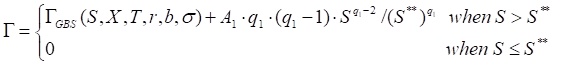
Vega
Call

Put

Theta
Call

where
ΘGBS - the generalized Black-Scholes call Θ expression.
Put

where
ΘGBS - the generalized Black-Scholes put Θ expression.
Rho
Call

where
ρGBS - the generalized Black-Scholes call ρ expression.
Put

where
ρGBS - the generalized Black-Scholes put ρ expression.
Implied volatility
System numerically finds implied volatility.
Implied volatility can’t be calculated for call option if option value is less than (underlying price - strike).
Implied volatility can’t be calculated for put option if option value is less than (strike - underlying).