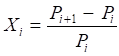
Historical Volatility measures the market’s past volatility. It is defined as the standard deviation of a series of price changes measured at regular intervals. It can be used in conjunction with Implied Volatility to gauge how the market’s current expectations differ from history.
The Historical Volatility display appears in a window below its corresponding chart. CQG allows the user to define the Historical Volatility using either Percent or Logarithmic price changes. Percent changes assume that prices change at fixed intervals. Logarithmic changes assume that prices are continuously changing. Although the logarithmic method may seem more appropriate, because it more accurately reflects an assumption of continuous trading, real world trading is not always continuous, so the Percent method may be more realistic.
High/Low Range changes use a different approach to the standard deviation way of calculating historical volatility. This approach uses high/low ranges that convey much more information than a simple chart of closing prices.
The following formulas are used to calculate Historical Volatility:
Percent
Price Changes
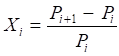
Logarithmic
Price Changes
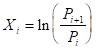
where P is the price at the end of each interval i
High/Low Range
Price Changes
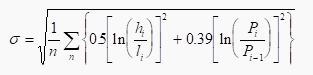
where:
n = period
h =
high price
l = low price
P is the price at the
end of each interval I
Mean
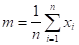
where m is the mean of n occurrences ( X )
Standard Deviation
Annualized Hvol
CQG annualizes Historical Volatility by multiplying the resulting Standard Deviation by the square root of the number of bars in a year. When a Daily Chart is displayed the system multiplies by square root of 252, Weekly by square root of 52, Monthly by square root of 12, Intraday by square root of (252 x Number of Bars Per Day).
Note: If these methods are compared to bank compounding of interest, at some point the differences between Regular Interval Compounding (Percent) and Continuous Compounding (Logarithmic) become very small.
Historical Volatility Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Display |
Opens sub-window to set parameters •Color = Line color. •Weight = Line thickness. •Display = Line style: line or histogram. •ShareScale = Determines whether sharing of the vertical scales between studies is accepted. Auto = System determine whether sharing is feasible. On = Scale is shared regardless of the functions and studies displayed. Off = Scale is not shared. ShareScale must be On if study is overlaid on a study with multiple outputs. |
|
MarkIt |
Opens Specify Conditions window. |
|
Type |
Historical volatility type. Values: •Percent •Log •Hi-Low Range |
|
Period |
Number of bars in the lookback range. |
|
Ann. Factor |
Number of trading days per year for the contract. To calculate bars per year, multiply this value by the bars per day. |
|
Price |
Price used to calculate study values. |