The document is an appendix to the main WebAPI proto file related to strategy trading parameters.
The corresponding settings of CQG IC Spreader are described at https://help.cqg.com/cqgic/25/Documents/settingspreadtradingparameters.htm.
For Smart Orders the corresponding settings are described at https://help.cqg.com/cqgic/25/#!Documents/smartorderspreferences.htm.
For Strategy Aggregation Parameters the corresponding settings are described at https://help.cqg.com/cqgic/25/#!Documents/marketmakingpassiveparameters2.htm.
•Rules to create a well-formed StrategyTradingParameters
•StrategyAggregationParameters
Rules to create a well-formed StrategyTradingParameters
To place an order on a synthetic strategy correctly, every NewOrder.Order message from the client side requires a well-formed StrategyTradingParameters:
1. MKT order must contain StrategyMarketOrderParameters message for every nonterminal strategy except aggregation.
2. STP order must contain StrategyStopOrderParameters for every nonterminal strategy except aggregation.
3. LMT order must contain:
1. StrategyLimitOrderParameters for every nonterminal strategy except aggregation.
2. StrategyLimitOrderParameters.LimitOrderLegDescription for every leg.
4. Every order with an aggregation strategy must contain:
1. StrategyAggregationParameters for every aggregation node..
2. StrategyAggregationParameters.AggregationLegDescription for every leg.
It is possible to get overfilled when the legs are being worked aggressively. Suppose you are working a 5-lot spread of 1:2, looking to be filled at 5:10. In actuality, you are filled at 7:10. This parameter specifies how to manage this overfill.
•MANUAL: Indicates that the trader manages the overfill and that the system should take no action.
•AUTOMATIC_HEDGING: Indicates that when either the working or leaning leg is overfilled, the system should try to maintain the leg ratio. In this example, the result is an order for four lots on the second leg.
•AVOID_OVERFILLS: Indicates that the system should minimize the chance for an overfill to occur by working legs less aggressively. Specifically, the system waits for the exchange to acknowledge its previous action before it adds quantity or places another order. Suitable only when working one leg of a spread.
In the case where you are overfilled one lot on the second leg, 5:11 for example, the system cannot hedge the spread because maintaining the ratio would require a half-lot order on the first leg.
Corresponds to CQG IC Overfill Management.
Calculates the corrected quantity ratio for each leg: corrected quantity ratio = total leg size / SS order size GW executes SS order using corrected leg quantity ratios.
Example: SPREAD(A-B,,,1:0.35), primary(working) leg is B, quantity rounding is ‘DOWN’. Strategy order is BUY 8 so by our rules we want to buy 8 A and sell 2 B. Corrected quantity ratios are 1 and 0.25. If 1 B lot is filled then the server places 4 lots on A (1/0.25 = 4 lots), despite the fact that original quantity ratio gives only two lots (1/0.35 = 2 lots).
•NONE: both primary and secondary leg orders could work its sizes proportionally (without aligning it to strategy lot).
•SECONDARY_ONLY: secondary leg orders must align its size to the strategy lots.
•ALL: both primary and secondary leg orders align its sizes to the strategy lots.
No CQG IC correspondence.
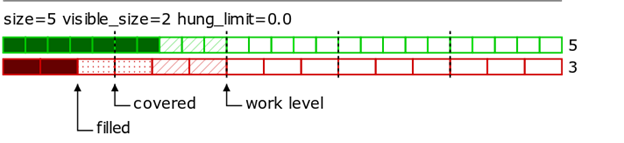
The parameter specifies the number of unbalanced (hung) strategy lots (maybe fractional) that don’t block raising the iceberg work level. Default parameter value is 0 which means that the next iceberg lots begin working only when at least one whole lot of the strategy is filled in the previous iceberg chunk.
In the following examples:
•spread with ratios 5:3 is shown;
•covered marks spread lots worked out by the primary (working) orders;
•work level shows the current level of the spread where the primary orders work;
•solid-filled cells are the filled leg lots;
•hatched cells are working leg lots (quoting orders);
•dotted cells are the leg lots with hedging orders, not filled yet;
•blank cells are lots with no orders no fills.

example1
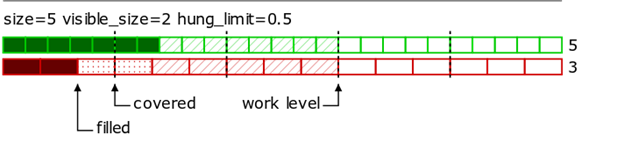
example2

example3
It’s best to explain this parameter through an example:
Suppose SPREAD(A-B,,,10:1) is being traded with A set as the working leg, Buy 1@10. After strategy order placement, the system works a primary order on A 10@100. Market B shows a best bid of 90. The order is partially filled 3@100 on A.
Market B then changes to 95, so the primary order is modified to 7@105. At this price, a second partial fill 6@105 occurs.
Market B returns to 90, and the last lot on A is filled with price 100. In total, we have 3 partial fills for the first leg: 3@100, 6@105 and 1@100.
Now the secondary order price needs to be chosen.
•AVERAGE_ORDER_PRICE calculates a secondary order price that would lead to a strategy order fill at the desired strategy price. First, the average fill price for the primary orders have to be calculated. Then, the secondary order price is calculated to satisfy the strategy price. This way of handling partial fills does help with strategy price execution, but sometimes leads to undesirable results. From our example: primary order average price = (3*100 + 6*105+1*100)/10 = 1030/10 = 103, thus secondary order price = A - S = 103-10 = 93, and a secondary order Sell 1@93 is placed. If market B shows a best bid of 1@90, that secondary order will likely hang.
•INDEPENDENT_LOT_PRICE tells the system to ignore fill prices on the primary orders. Instead, the secondary order is placed to hit the opposite market side. In this case, strategy price execution cannot be guaranteed, but hang probability is decreased. From our example: if market B shows a best bid of 1@91, a secondary order Sell 1@91 is placed.
Corresponds to CQG IC Ignore partial fills.
Sets the dynamic change of the strategy price depending on filled lots, i.e. after each filled_qty_delta lots of the strategy order are filled the limit price for the rest of the order is changed by some constant offset price_step.
No CQG IC correspondence.
Indicates what percentage of contracts should be filled before the second leg order is placed. For example, you’re working 10 lots of TYA and leaning on 1 million of BTC. If this setting is 50%, then the BTC leg order should be placed when 5 lots of TYA have been filled.
Corresponds to CQG IC Proportional Execution Parameters.
Determines the size of working orders based on a percentage of the resting volume available in the queue of the monitored leg. For example, if set to 2, then twice as many contracts must be available in the monitored leg than the working leg. If there is not enough resting volume, the working order is placed with a smaller size or not placed at all. Allowed values: 0.1 to 999.9. Default = 1.
Corresponds to CQG IC Liquidity Controls/Volume Multiplier.
Tells the system to work the order if and only if the available quantity in the monitored leg is and remains greater than this value. The system works the order only for the quantity that exceeds this threshold. Example: if Working Threshold = 5 and Available Quantity = 7, then Order Quantity = 2. Allowed values: -9999 to 9999. Default = 0.
Corresponds to CQG IC Liquidity Controls/Work Threshold.
Indicates the legs to work.
Minimizes transaction count. Tells the system to place an order only if the quantity available in the monitored leg is at least this much and to modify a working order only if the quantity available in the monitored leg increases by at least this much. This parameter is applied to the working order only when the monitored available quantity increases; the working order size is always modified on a decrease in the available quantity on the monitored side. Applies to working orders. In lots.
Corresponds to CQG IC Min Size Increment.
queue_holders_min_size, queue_holders_max_size
Sets the minimum and maximum number of orders to include in the queue. For example, a setting of 5 and 9 indicates that the minimum number of price levels (i.e. the minimum number of stacked orders) is 5 and the maximum number of price levels is 9. The system cancels the stacked orders when a leg is filled. Risk management margin requirements are calculated assuming that all of the orders have the potential to fill. Allowed values: 1-10. Default = 1.
Corresponds to CQG IC Min number of holders and Max number of holders.
Indicates how many price levels to skip between orders in the queue. For example, a setting of 3 indicates that an order be placed at every third price level. Allowed values: 1-5. Default = 1.
Corresponds to CQG IC Number of levels to skip between queue holders.
Indicates how far the market should run before maximizing the size of a recently placed order that is now part of the group of stacked orders. The size of the working order is based on the currently available size in the monitored leg and the size of the orders in the group of stacked orders at the maximum order size. This setting overrides that system behavior in order to cut down on messaging. For example, a setting of 3 tells the system to update the order quantity in the queue only when the market moves 3 price levels.
Default = 0
The value for this parameter must be less than the smallest number in queue_holders_min_size. So, if queue_holders_min_size = 5-9, then order_size_restore_threshold ≤ 4.
Corresponds to CQG IC Order size restore threshold.
Sets a visible iceberg order size.
Corresponds to CQG IC Smart Orders/Enter a visible order size.
Sets random iceberg order sizes between this value and visible_qty.
Corresponds to CQG IC Smart Orders/Random order sizes.
Defines the range (from best bid/best offer whichever is closest) where orders are actively worked in ticks.
Values:
•Default = do not override server setting
•0 = no limit
•1-10, 20, 30
Corresponds to CQG IC Active Price Range.
Minimum price change to update the working leg order price in price increments. The system ignores any price changes that are smaller in price increments than this value.
Values:
•not set - do not override server settings
•1-9
Corresponds to CQG IC Min Price Change.
primary_orders_fifo_queue_size
Defines the maximum allowed number of working orders for one price level (queue_holders_* parameters). If total size on a price level is to be increased then:
•a new order must be added to the level if the number of orders on the level is less than specified:
•otherwise the size of the last placed order on this level must be increased.
No CQG IC correspondence.
Period of updates to the working leg in seconds, such that every N seconds the leg is put where it ought to be placed based upon current prices.
Values:
•not set - do not override server settings.
•any other value up to 3600.
Corresponds to CQG IC Periodic Force Update.
Shows whether observed markets must be used for primary orders size calculation or not.
No CQG IC correspondence.
Specifies (in ticks) the maximum distance a primary order price could be moved from the target one while creating a best bid/ask.
No CQG IC correspondence.
Determines how the working legs that are far from the market are handled. A working leg is considered far from the market if its price is less than (for buy) or greater than (for sell) the market price by the number of ticks specified in Active Price Range.
•not set - do not override server settings.
•NO_ORDERS cancels leg right away.
•DONT_MOVE keeps the order wherever it is and move it only when the time comes for a periodic update.
•MOVE_AWAY_ONLY keeps it wherever it is but moves away from the market every time it should be further away and do periodic updates to move it closer to the market.
Corresponds to CQG IC Order Action outside active range.
Ticks away to work at additional level: defines if and where Spreader must work quantity that cannot lean onto the current best bid/offer. For example, when the order is to work 100 of 1:1 but only 23 is available on leaning leg, Spreader works 23 on the working leg when this parameter is set to 0. If it’s set to 2, Spreader works 23 and then additional 77 2 ticks away.
Values:
•Not set = do not override server setting.
•0-9
Corresponds to CQG IC Price Level Controls.
How to work orders considering depth of market
•TOP_ONLY: Work order based on the BBA.
•MULTILEVELS: Work up to dom_multilevel_qty number of orders to get required volume.
•FULL_SIZE_WORST_PRICE: Work single order based on the leaning leg price with the required volume.
•FULL_SIZE_AVERAGE_PRICE: Work single order based on the average of the leaning leg prices with required volume.
Corresponds to CQG IC How to work orders considering depth of market.
Work up to this number of orders to get required volume if dom_usage is MULTILEVELS. Allowed range 1-10, default is 1.
Corresponds to CQG IC How to work orders considering depth of market.
Identifies the limit type for orders placed on this leg as a result of a working leg fill
Identifies a limit order placed at the normally calculated price +/- the specified offset.
Corresponds to CQG IC Complete strategy using limit with offset (LMT with offset).
Replaces the original limit order to complete the spread with a limit order that has the price adjusted based on number of slip ticks. The replacement can happen based on one of the specified conditions: either timeout or DOM volume.
The price offset to modify when the payup condition (time and/or one of the leaning DOM volume options) is met.
Corresponds to CQG IC Allow leg to slip this number of ticks.
The price offset to adjust the secondary order price at the moment of placement.
No CQG IC correspondence.
Indicates the amount of time that must elapse from acknowledgement before the incomplete strategy is executed. It allows you, for example, to wait a second to see if the market comes back. Default = 0.
Corresponds to CQG IC Execute incomplete strategy if order is not filled in this many seconds.
Uses the parameter as an absolute volume (allowed values 1-9999). When the leaning leg volume available at the exchange (best bid/ask, as appropriate for a leaning sell/buy order) drops below this specified volume, then the system performs a payup (replaces the original limit order to complete the spread with a limit order that has the price adjusted based on specified number of slipped ticks) or a trailing limit.
Corresponds to CQG IC DOM Volume.
condition_opposite_volume_ratio
Uses the parameter as a volume ratio (allowed values 0.1 – 999.9). When the ratio between the volume available at the exchange (best bid/ask, as appropriate for a leaning sell/buy order) and the leaning leg order size falls below the specified ratio, then the system performs a payup (replaces the original limit order to complete the spread with a limit order that has the price adjusted based on a specified number of slipped ticks) or a trailing limit.
Corresponds to CQG IC DOM Volume relative to order size.
Uses the parameter as a volume ratio (allowed values 0.1 – 999.9). When the ratio between volumes available at the exchange (best bid/ask for a leaning sell order, best ask/bid for a leaning buy order) falls below the specified ratio, then the system performs a payup (replaces the original limit order to complete the spread with a limit order that has the price adjusted based on specified number of slipped ticks) or a trailing limit.
Corresponds to CQG IC DOM ratio between best bid/ask.
Determines whether the system should react to incomplete orders with trailing limits.
Indicates the maximum price offset of slippage for the incomplete strategy. Can be a positive or negative value.
Corresponds to CQG IC Allow leg to slip this number of ticks.
•same side as the order: places a trailing limit order that tracks the same side as the incomplete order. For example, if the sell side is incomplete, then it trails the offer. If the monitor DOM volume option is selected, the DOM condition must be met before trailing occurs.
•opposite side: places a trailing limit order that tracks the opposite side of the incomplete order. For example, if the sell side is incomplete, then it trails the bid. If the monitor DOM volume option is selected, the DOM condition must be met before trailing occurs.
Corresponds to CQG IC Allow leg to slip this number of ticks.
The price offset to adjust the secondary order price at the moment of placement.
No CQG IC correspondence.
The maximum distance to trail away from the initial price (positive double). Default value is no limit of order trailing.
No CQG IC correspondence.
Same as SecondaryOrdersPayUp.condition_absolute_volume.
condition_opposite_volume_ratio
Same as SecondaryOrdersPayUp.condition_opposite_volume_ratio.
Same as SecondaryOrdersPayUp.condition_bba_volume_ratio.
The overfill mode governs how the server reacts when your target price becomes available on a leg and the leg is working less than the available quantity. Example: If you place an order to buy 10 AGGR(A&B) @ LMT 8 and the best ask on both A and B is greater than 8, assuming the Trading Distribution for A = 80% and B = 20%, the server works Leg 1 (buy 8A @ 8) and Leg 2 (buy 2B @ 8). If the best ask for B moves down to 7 offered @ 8 (the target price), the server needs to modify Leg 1 from 8 to 3 and place a new order on Leg 2 (buy 5B @ 8) in order to get the 7 available at the target price.
•AVOID_OVERFILLS: In this mode, the server does not place the second order on Leg 2 until it has received an acknowledgement of the reduction (by cancel or modify) of the Leg 1 order.
•ACCEPT_OVERFILL: In this mode, the server places the second order on Leg 2 and only then attempts to reduce the quantity on Leg 1.
•PRESERVE_QUEUE_POSITION: In this mode, the server places the second order on Leg 2 and then reduces the quantity on Leg 1 only when the Leg 2 orders have been filled.
Corresponds to CQG IC Market Making/Passive Parameters, Overfills.
Sets the dynamic change of the strategy price depending on filled lots, i.e. after each filled_qty_delta lots of strategy order are filled the limit price for the rest of the order is changed by some constant offset price_step.
No CQG IC correspondence.
This parameter, set independently for each leg, defines a threshold quantity that the server ignores for purposes of determining available quantity on that leg. (e.g. If the best ask is 10@8 and the threshold quantity is 10, then the server treats the best ask as 0@8 and does not place any taking orders on that leg.)
Corresponds to CQG IC Work Threshold.
Market Taking mode indicates that your order is held on the server until your price becomes available in at least one market; at which time, the server sends an order to the exchange.
Allows you to specify how many lots are placed on each leg provided there is sufficient volume at your target price.
In the event that there is NOT sufficient volume at your target price in one or more legs, this preference is ignored, and the server attempts to fill your order at your target price without regard to market preference.
The allocations for Market Taking can be different from those set for Market Making.
The allocations for Market Taking must equal 1.
Corresponds to CQG IC Preferred Market %.
Allows you to set how long to work a taking order.
This parameter, set independently for each leg, controls the amount of time that the server allows a taking order to work (after exchange acknowledgment) before considering it timed out (and thus canceling it).
Default = 0. Zero means that the server never cancels an unfilled taking order.
Corresponds to CQG IC Partial fills: how long to work a taking order.
This parameter, set independently for each leg, controls the order type (LMT v. MKT) that the server uses for any taking order.
Corresponds to CQG IC Order Type.
Market Making mode indicates that your order is sent immediately to the exchanges based on your trading distribution preferences. The server then manages your orders to get you filled as quickly as possible at your price.
Allows you to specify how much of the Aggregation Order is placed on each leg. You can set the percentage allocation up to 1 on each leg. In the event that the target price appears on a leg that is working less than the total order size, the server shifts orders to that leg in accordance with overfill_mode.
Example: If you place an order to buy 10 AGGR(A&B) and your Trading Distribution is set to 0.5 - 0.5, the server places 5 lots on A and 5 lots on B. The server then works your orders (shifting markets if necessary) as you receive fills. Alternatively, if your Trading Distribution is set to 1 - 1, the server places 10 lots on A and 10 lots on B and then works your orders (canceling orders as necessary) as you receive fills.
Corresponds to CQG IC Preferred Market %.
Sets a visible iceberg order size.
Corresponds to CQG IC Smart Orders/Enter a visible order size.
Sets random iceberg order sizes between this value and visible_qty.
Corresponds to CQG IC Smart Orders/Random order sizes.
When the strategy order is Iceberg, use limits for orders with this size or fewer.
No CQG IC correspondence.